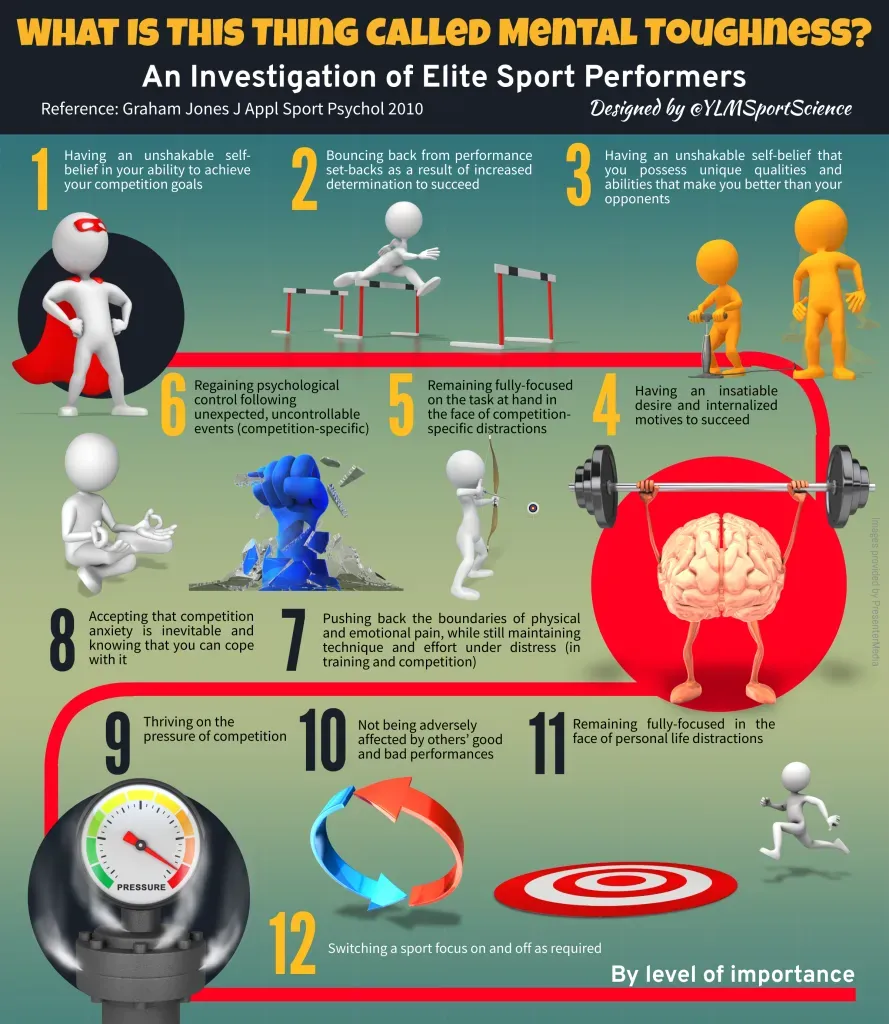
Mental Toughness in Sports is a learnable skill set that separates champions from hopefuls when the arena grows loud and the clock ticks down. In high-stakes arenas, under pressure performance in sports hinges on staying calm, focused, and composed rather than succumbing to fear or doubt. This introductory piece blends practical techniques like visualization in sports, breathing techniques for athletes, and pre-game routines for focus into a cohesive mental training plan. By reinforcing psychological resilience in athletes, you build a robust toolkit that translates to real results when the stakes are highest. The aim is to convert pressure into purposeful action, creating consistent execution when it matters most.
Viewed through another lens, this capability becomes cognitive stamina, inner fortitude, and emotional regulation that keep athletes poised when crowds roar. LSI principles point to related terms such as mental conditioning, adaptive focus, and resilience under pressure, linking science to actionable training. In practice, you’re nurturing neural readiness, strategic composure, and habit formation that support consistent performance across sports. Recovery practices and sleep quality also feed into this broader picture, strengthening mood, decision speed, and focus. By layering these synonyms with your familiar routines, you build a more complete blueprint for performing confidently when it truly counts.
Mental Toughness in Sports: Core Pillars and How to Build Them
Mental toughness in sports centers on stabilizing confidence, focus, and emotional control when outcomes are uncertain. The three core pillars—belief in the ability to control the controllables, effective emotional regulation, and decision-making under stress—guide how athletes respond to pressure. This framework supports better under-pressure performance in sports and a steadier course through mistakes and setbacks.
To build these pillars, practitioners should blend deliberate practice with reflective routines. Develop psychological resilience in athletes by setting small, repeatable challenges that reinforce composure, then scale them as skills become automatic. Visualization in sports, breathing techniques for athletes, and structured feedback loops help embed responses that stay consistent when crowds roar or game tempo accelerates.
Visualization in Sports: Training the Brain to Expect Success
Visualization in sports is more than wishful thinking; it trains brain–muscle coordination by rehearsing precise movements, timing, and pressure responses. Athletes who regularly picture successful outcomes activate neural patterns that resemble real performance, speeding reaction times and sharpening focus during critical moments.
A practical approach blends vivid sensory details with real cues from upcoming competition. Pair imagery with on-field practice so imagined scenarios align with actual play, helping you trust your instincts when the game speeds up. Regular visualization complements breathing techniques for athletes and supports the broader goal of achieving consistent under-pressure performance.
Breathing Techniques for Athletes: Regulating Arousal for Peak Performance
Breathing techniques for athletes address the physiological arousal that can derail performance. Diaphragmatic breathing, extended exhalations, and paced patterns help lower heart rate, reduce muscle tension, and sharpen concentration, especially during pivotal moments.
A simple routine such as box breathing—inhale for four counts, hold, exhale for four, and hold again for four—can be used before a key play or during a timeout to regain calm. These techniques are portable and quick to deploy, making them a cornerstone of mental training for athletes seeking to optimize under pressure performance in sports.
Pre-Game Routines for Focus: Building Predictability and Confidence
Pre-game routines for focus create a stable mental environment by signaling readiness and anchoring attention. A well-crafted ritual might include a short warm-up, ball-handling drills, a brief visualization, a specific song, or cue-based self-talk that primes the brain for competition.
The key is consistency—perform the same routine in the same order every time, regardless of opponent or venue. When pressure rises, this ritual becomes a familiar shoreline, reducing anxiety and enabling sharper execution, while also reinforcing psychological resilience in athletes across different settings.
Positive Self-Talk and Confidence: Building a Resilient Inner Dialogue
Positive self-talk shapes how stress is interpreted and how performance unfolds. Shifting from catastrophic thoughts to task-focused cues reframes pressure as a sequence of controllable actions. Developing a bank of present-tense phrases—such as “I’ve prepared,” “I can handle this,” or “One play at a time”—helps sustain focus during high-stakes moments.
Coupled with mindful reflection, this practice supports psychological resilience in athletes by identifying automatic negative thoughts and replacing them with constructive, performance-enhancing perspectives. The goal is not to deny fear but to channel it into disciplined action consistent with training and tactical intent.
Handling Mistakes and Bounce-Back: Fast Reset for Continuous Momentum
Mistakes happen to every champion; what matters is how quickly you reset and recover. A rapid “reset protocol”—acknowledge the error, reframe it as information, take a breath, and commit to the next action—helps minimize a negative spiral and maintains progress toward the game plan.
Practicing this bounce-back mindset during training accelerates the transfer to competition. By treating mistakes as learnable data rather than personal failures, athletes reinforce under-pressure performance in sports and strengthen psychological resilience in athletes, keeping performance trajectories steady even when outcomes tilt unfavorably.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mental Toughness in Sports and how does it influence under pressure performance in sports?
Mental Toughness in Sports is a learnable set of skills that help you stay confident, focused, and emotionally regulated when the outcome is uncertain. It drives under pressure performance in sports by strengthening belief in controllables, emotional regulation, and decision-making under stress. Build it by practicing psychological resilience in athletes through realistic pressure simulations, pairing visualization in sports with breathing techniques for athletes, and establishing a consistent pre-game routine for focus. Track progress across practices and games.
How can psychological resilience in athletes be developed to improve performance under pressure?
Psychological resilience in athletes is built by training the mind like the body: cultivate belief in controllables, rehearse coping strategies, and ensure recovery supports brain function. Use stress inoculation by simulating late-game pressure in practice, implement short post-practice reflections to reframe negative thoughts, and reinforce positive self-talk. Pair these with proper sleep, recovery, and nutrition to sustain cognitive performance under pressure.
How does visualization in sports contribute to calm and precise execution during critical moments?
Visualization in sports primes the brain and nervous system to rehearse exact movements, timing, and responses to pressure, helping you stay calm when the game speeds up. Develop a vivid routine: close your eyes, breathe calmly, and imagine a specific moment with sensory details, then translate that imagery into on-field practice to align cues with real signals.
What breathing techniques for athletes are most effective for regulating arousal during key moments?
Breathing techniques for athletes that work include diaphragmatic breathing and box breathing. Diaphragmatic breathing reduces physical arousal, while box breathing (inhale 4, hold 4, exhale 4, hold 4) can reset your nervous system before pivotal moments or timeouts, helping you stay focused and steady.
How can pre-game routines for focus be designed to stabilize attention and consistency across games?
Pre-game routines for focus create predictable cues that put your brain into competition mode. Build a routine with warm-ups, ball handling, a short visualization, and cue-based self-talk; perform it the same way every game to reduce anxiety and improve consistency, even when environment changes.
What practical plan combines visualization in sports, breathing techniques for athletes, and pre-game routines for focus into a mental training program?
Design a practical mental training plan by starting with a baseline and selecting two techniques to practice for four weeks (for example, visualization in sports and breathing techniques for athletes). Practice daily, log moments of technique use, pressure level, and outcomes, then add one more technique (such as pre-game routines for focus) and reassess. Treat mental training as part of your overall program alongside physical skill and tactical work to improve under-pressure performance.
| Key Concept | What It Means | Practical Techniques | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mental Toughness in Sports | Capacity to stay confident, focused, and regulate emotions under pressure | Remain calm and focused; maintain moment-to-moment control | More consistent performance in critical moments |
| Pillars | Belief in controllables, emotional regulation, and decision-making under stress | Develop these through deliberate practice and reflection | Greater stability and resilience |
| Visualization and imagery | Mental rehearsal of precise movements and responses | Close eyes, imagine specific moments with sensory detail; align with cues | Improved reaction times and sharper focus |
| Breathing techniques | Regulate arousal, lower heart rate, reduce tension | Box breathing; diaphragmatic and paced breathing | Calm, precise execution under pressure |
| Pre-game routines | Create consistency and readiness cues | Warm-ups, visualization, self-talk cues | Predictable focus and reduced anxiety |
| Positive self-talk | Shift from catastrophic thinking to task-focused thoughts | Use present-tense, concise affirmations | Increased confidence during pressure |
| Handling mistakes | Rapid error recognition and corrective action | Reset protocol within 10–15 seconds after an error | Prevents negative spirals and maintains momentum |
| Stress inoculation | Progressive exposure to higher-stakes situations | Simulated late-game scenarios in practice | Builds confidence and composure |
| Sleep and recovery | Recovery and nutrition influence cognitive function | Prioritize sleep, hydration, and balanced meals | Sustained attention and faster decision-making |
| Practical training plan | Progressive integration into routine | Baseline assessment; choose two techniques; track progress | Clear path to improvement and accountability |
Summary
Conclusion: Mental Toughness in Sports is a powerful, learnable blueprint for winning under pressure. By combining visualization, breathing, pre-game routines, positive self-talk, and robust recovery practices, athletes can build a resilient mindset that remains steady when the stakes rise. This mental training approach complements physical conditioning and technical skill, reinforcing performance consistency across sports. With deliberate practice and a structured plan, you can translate mental resilience into tangible on-field results, approaching high-pressure moments with confidence, clarity, and the poise to execute your game plan.